arduino教程系列28-ITG3200 ADXL345做姿态识别实验
姿态识别应用范围很广,像自平衡车呀,飞行器呀,双足机器人呀之类。本次我们使用Arduino+ITG3205+ADXL345做姿态检测,使用Processing作为输出,实时显示姿态。
本次实验使用的ITG3205与ADXL345都是成品模块,都可以使用I2C接口进行连接。
先看硬件连接,模拟5号口连接I2C模块的SCL,模拟4号口连接I2C模块的SDA口。VCC与GND正常连接,主要不要接错电压,要使用3.3V。I2C模块之间并联。
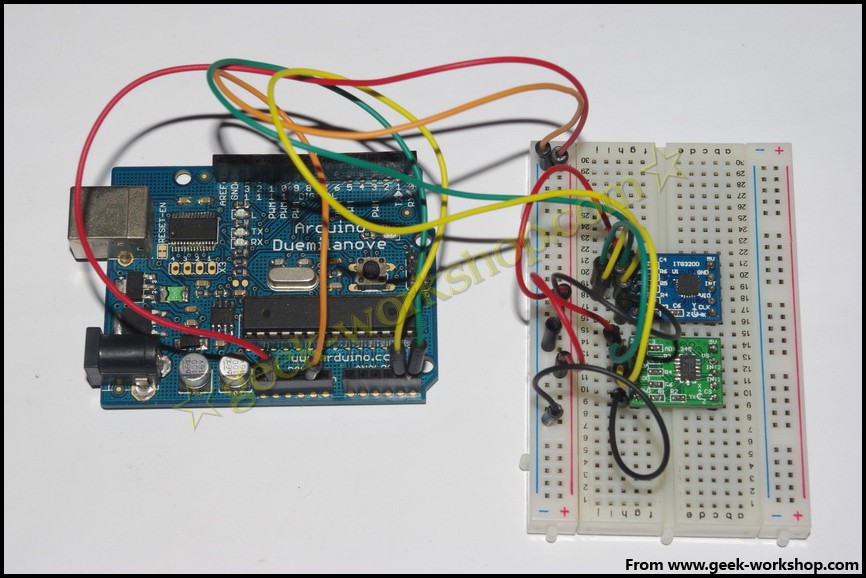
2011-11-25 21:09 上传
(124.68 KB)
arduino实验
把下面的代码编译后下载进入arduino控制板中。ARDUINO 代码复制打印
#include <Wire.h> // 调用I2C库
// 加速度传感器 ADXL345
#define ACC (0x53) //定义ADXL345地址
#define A_TO_READ (6) //读取每次占用的字节数 (每个坐标轴占两个字节)
// 陀螺仪 ITG3200
#define GYRO 0x68 // 定义传感器地址,将AD0连接到GND口,传感器地址为二进制数11101000 (请参考你接口板的原理图)
#define G_SMPLRT_DIV 0x15
#define G_DLPF_FS 0x16
#define G_INT_CFG 0x17
#define G_PWR_MGM 0x3E
#define G_TO_READ 8 // x,y,z 每个轴2 bytes
// 陀螺仪误差修正的偏移量
int g_offx = 67;
int g_offy = 5;
int g_offz = 41;
// 加速度传感器误差修正的偏移量
int a_offx = -30;
int a_offy = -8;
int a_offz = 0;
char str[512];
void initAcc() {
//调用 ADXL345
writeTo(ACC, 0x2D, 0);
writeTo(ACC, 0x2D, 16);
writeTo(ACC, 0x2D, 8);
//设定在 +-2g 时的默认读数
}
void getAccelerometerData(int * result) {
int regAddress = 0x32; //加速度传感器ADXL345第一轴的数据的设定
byte buff[A_TO_READ];
readFrom(ACC, regAddress, A_TO_READ, buff); //读取加速度传感器ADXL345的数据
//每个轴的读数有10位分辨率,即2个字节.
//我们要转换两个bytes为一个int变量
result[0] = (((int)buff[1]) << 8) | buff[0] + a_offx;
result[1] = (((int)buff[3]) << 8) | buff[2] + a_offy;
result[2] = (((int)buff[5]) << 8) | buff[4] + a_offz;
}
//初始化陀螺仪
void initGyro()
{
/*****************************************
* ITG 3200
* 电源管理设定:
* 时钟选择 =内部振荡器
* 无复位, 无睡眠模式
* 无待机模式
* 采样率 = 125Hz
* 参数为+ / - 2000度/秒
* 低通滤波器=5HZ
* 没有中断
******************************************/
writeTo(GYRO, G_PWR_MGM, 0x00);
writeTo(GYRO, G_SMPLRT_DIV, 0x07); // EB, 50, 80, 7F, DE, 23, 20, FF
writeTo(GYRO, G_DLPF_FS, 0x1E); // +/- 2000 dgrs/sec, 1KHz, 1E, 19
writeTo(GYRO, G_INT_CFG, 0x00);
}
void getGyroscopeData(int * result)
{
/**************************************
* 陀螺仪ITG- 3200的I2C
* 寄存器:
* temp MSB = 1B, temp LSB = 1C
* x axis MSB = 1D, x axis LSB = 1E
* y axis MSB = 1F, y axis LSB = 20
* z axis MSB = 21, z axis LSB = 22
*************************************/
int regAddress = 0x1B;
int temp, x, y, z;
byte buff[G_TO_READ];
readFrom(GYRO, regAddress, G_TO_READ, buff); //读取陀螺仪ITG3200的数据
result[0] = ((buff[2] << 8) | buff[3]) + g_offx;
result[1] = ((buff[4] << 8) | buff[5]) + g_offy;
result[2] = ((buff[6] << 8) | buff[7]) + g_offz;
result[3] = (buff[0] << 8) | buff[1]; // 温度
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Wire.begin();
initAcc();
initGyro();
}
void loop()
{
int acc[3];
int gyro[4];
getAccelerometerData(acc);
getGyroscopeData(gyro);
sprintf(str, "%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d,%d", acc[0], acc[1], acc[2], gyro[0], gyro[1], gyro[2], gyro[3]);
Serial.print(str);
Serial.print(10, BYTE);
//延时50毫秒
}
//---------------- 功能
//将val写入到加速度传感器的地址寄存器中
void writeTo(int DEVICE, byte address, byte val) {
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE); //传送到加速度传感器
Wire.send(address); // 发送寄存器地址
Wire.send(val); // 发送要写入的值
Wire.endTransmission(); //结束传输
}
//加速度传感器在地址寄存器的缓冲区阵列中读取读数
void readFrom(int DEVICE, byte address, int num, byte buff[]) {
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE); //开始传送至加速度传感器
Wire.send(address); //发送读取的地址
Wire.endTransmission(); //结束传输
Wire.beginTransmission(DEVICE); //开始传送到ACC
Wire.requestFrom(DEVICE, num); // 要求从加速度传感器中发送6个字节的数据
int i = 0;
while(Wire.available()) //当加速度传感器返回的数据小于要求值时(异常情况)
{
buff[i] = Wire.receive(); // 接收数据
i++;
}
Wire.endTransmission(); //结束传输
}
先介绍一下processing的基本使用方法,先从http://processing.org/download/下载回来processing的IDE。
然后把下面代码拷贝进入进入processing,查看连接arduino的com口是第几个。根据具体情况调整com口连接代码。ARDUINO 代码复制打印
import processing.serial.*;
Serial myPort; // 创建串口对象myPort
boolean firstSample = true;
float [] RwAcc = new float[3]; // 通过加速度传感器把重力加速度投影在x/y/z三轴上
float [] Gyro = new float[3]; // 陀螺仪读取
float [] RwGyro = new float[3]; // 重新读取陀螺仪
float [] Awz = new float[2]; // XZ/ YZ平面和Z轴(度)R的投影之间的角度
float [] RwEst = new float[3];
int lastTime = 0;
int interval = 0;
float wGyro = 10.0;
int lf = 10; // 10在ASCII表中表示'\n'
byte[] inBuffer = new byte[100];
PFont font;
final int VIEW_SIZE_X = 600, VIEW_SIZE_Y = 600;
void setup()
{
size(VIEW_SIZE_X, VIEW_SIZE_Y, P3D);
myPort = new Serial(this, Serial.list()[2], 9600); // 设置电脑第三个COM口为连接端口,这个要根据你电脑情况进行设置。
//myPort = new Serial(this, "/dev/ttyUSB0", 9600);
// 加载字体,字体必须在代码文件同目录下的data文件夹中
font = loadFont("CourierNew36.vlw");
}
void readSensors() {
if (myPort.available() > 0) {
if (myPort.readBytesUntil(lf, inBuffer) > 0) {
String inputString = new String(inBuffer);
String [] inputStringArr = split(inputString, ',');
// 把原始数据转换为G
RwAcc[0] = float(inputStringArr[0]) / 256.0;
RwAcc[1] = float(inputStringArr[1])/ 256.0;
RwAcc[2] = float(inputStringArr[2])/ 256.0;
// 把原始数据转换为"度/秒"
Gyro[0] = float(inputStringArr[3]) / 14.375;
Gyro[1] = float(inputStringArr[4]) / 14.375;
Gyro[2] = float(inputStringArr[5]) / 14.375;
}
}
}
void normalize3DVec(float [] vector) {
float R;
R = sqrt(vector[0]*vector[0] + vector[1]*vector[1] + vector[2]*vector[2]);
vector[0] /= R;
vector[1] /= R;
vector[2] /= R;
}
float squared(float x) {
return x*x;
}
void buildBoxShape() {
//box(60, 10, 40);
noStroke();
beginShape(QUADS);
//Z+ (绘图区域)
fill(#00ff00);
vertex(-30, -5, 20);
vertex(30, -5, 20);
vertex(30, 5, 20);
vertex(-30, 5, 20);
//Z-
fill(#0000ff);
vertex(-30, -5, -20);
vertex(30, -5, -20);
vertex(30, 5, -20);
vertex(-30, 5, -20);
//X-
fill(#ff0000);
vertex(-30, -5, -20);
vertex(-30, -5, 20);
vertex(-30, 5, 20);
vertex(-30, 5, -20);
//X+
fill(#ffff00);
vertex(30, -5, -20);
vertex(30, -5, 20);
vertex(30, 5, 20);
vertex(30, 5, -20);
//Y-
fill(#ff00ff);
vertex(-30, -5, -20);
vertex(30, -5, -20);
vertex(30, -5, 20);
vertex(-30, -5, 20);
//Y+
fill(#00ffff);
vertex(-30, 5, -20);
vertex(30, 5, -20);
vertex(30, 5, 20);
vertex(-30, 5, 20);
endShape();
}
void drawCube() {
pushMatrix();
translate(300, 450, 0);
scale(4, 4, 4);
rotateX(HALF_PI * -RwEst[0]);
rotateZ(HALF_PI * RwEst[1]);
buildBoxShape();
popMatrix();
}
void getInclination() {
int w = 0;
float tmpf = 0.0;
int currentTime, signRzGyro;
readSensors();
normalize3DVec(RwAcc);
currentTime = millis();
interval = currentTime - lastTime;
lastTime = currentTime;
if (firstSample || Float.isNaN(RwEst[0])) { // NaN用来等待检查从arduino过来的数据
for (w=0;w<=2;w++) {
RwEst[w] = RwAcc[w]; // 初始化加速度传感器读数
}
}
else {
// 对RwGyro进行评估
if (abs(RwEst[2]) < 0.1) {
// Rz值非常的小,它的作用是作为Axz与Ayz的计算参照值,防止放大的波动产生错误的结果。
// 这种情况下就跳过当前的陀螺仪数据,使用以前的。
for (w=0;w<=2;w++) {
RwGyro[w] = RwEst[w];
}
}
else {
// ZX/ZY平面和Z轴R的投影之间的角度,基于最近一次的RwEst值
for (w=0;w<=1;w++) {
tmpf = Gyro[w]; // 获取当前陀螺仪的deg/s
tmpf *= interval / 1000.0f; // 得到角度变化值
Awz[w] = atan2(RwEst[w], RwEst[2]) * 180 / PI; // 得到角度并转换为度
Awz[w] += tmpf; // 根据陀螺仪的运动得到更新后的角度
}
// 判断RzGyro是多少,主要看Axz的弧度是多少
// 当Axz在-90 ..90 => cos(Awz) >= 0这个范围内的时候RzGyro是准确的
signRzGyro = ( cos(Awz[0] * PI / 180) >=0 ) ? 1 : -1;
// 从Awz的角度值反向计算RwGyro的公式请查看网页 http://starlino.com/imu_guide.html
for (w=0;w<=1;w++) {
RwGyro[0] = sin(Awz[0] * PI / 180);
RwGyro[0] /= sqrt( 1 + squared(cos(Awz[0] * PI / 180)) * squared(tan(Awz[1] * PI / 180)) );
RwGyro[1] = sin(Awz[1] * PI / 180);
RwGyro[1] /= sqrt( 1 + squared(cos(Awz[1] * PI / 180)) * squared(tan(Awz[0] * PI / 180)) );
}
RwGyro[2] = signRzGyro * sqrt(1 - squared(RwGyro[0]) - squared(RwGyro[1]));
}
// 把陀螺仪与加速度传感器的值进行结合
for (w=0;w<=2;w++) RwEst[w] = (RwAcc[w] + wGyro * RwGyro[w]) / (1 + wGyro);
normalize3DVec(RwEst);
}
firstSample = false;
}
void draw() {
getInclination();
background(#000000);
fill(#ffffff);
textFont(font, 20);
//float temp_decoded = 35.0 + ((float) (temp + 13200)) / 280;
//text("temp:\n" + temp_decoded + " C", 350, 250);
text("RwAcc (G):\n" + RwAcc[0] + "\n" + RwAcc[1] + "\n" + RwAcc[2] + "\ninterval: " + interval, 20, 50);
text("Gyro (°/s):\n" + Gyro[0] + "\n" + Gyro[1] + "\n" + Gyro[2], 220, 50);
text("Awz (°):\n" + Awz[0] + "\n" + Awz[1], 420, 50);
text("RwGyro (°/s):\n" + RwGyro[0] + "\n" + RwGyro[1] + "\n" + RwGyro[2], 20, 180);
text("RwEst :\n" + RwEst[0] + "\n" + RwEst[1] + "\n" + RwEst[2], 220, 180);
// display axes显示轴
pushMatrix();
translate(450, 250, 0);
stroke(#ffffff);
scale(100, 100, 100);
line(0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0);
line(0, 0, 0, 0, -1, 0);
line(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1);
line(0, 0, 0, -RwEst[0], RwEst[1], RwEst[2]);
popMatrix();
drawCube();
}
然后点击运行
实验效果: