arduino教程系列27-DS1307 RTC时钟芯片与DS18B20数字温度传感器实验 温度传感器,芯片
本次实验我使用的是购买的一个DS1307 RTC模块,上面集成了一个DS18B20温度传感器,还集成了另外一个存储芯片~~
先上图
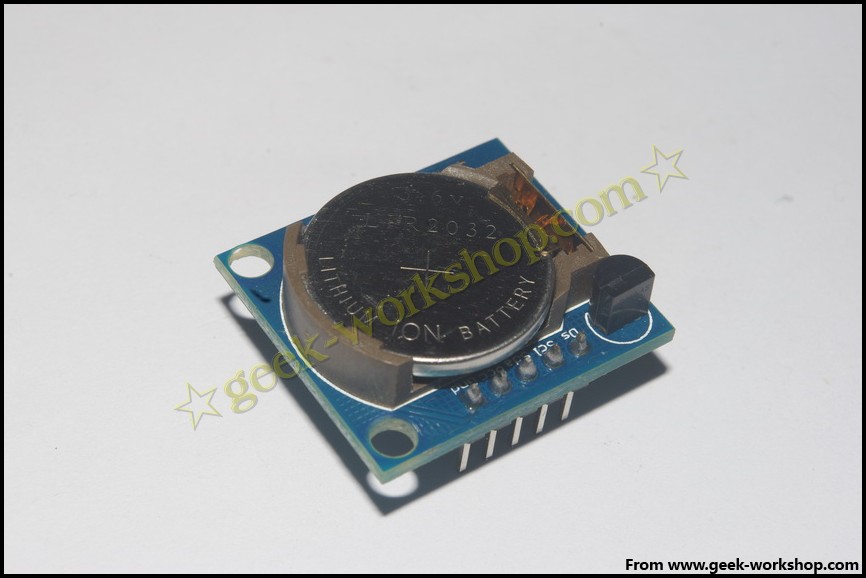

2011-11-17 22:28 上传
(65.25 KB)
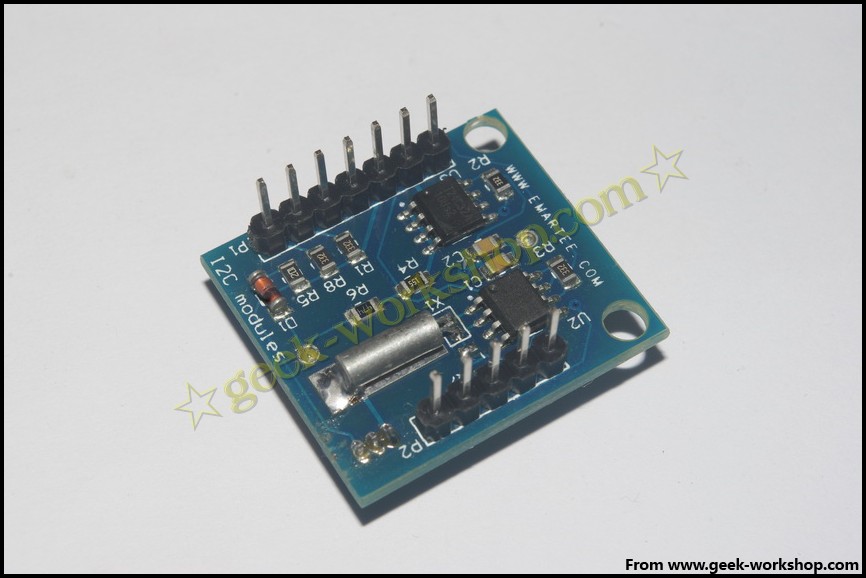

2011-11-17 22:28 上传
(76.97 KB)
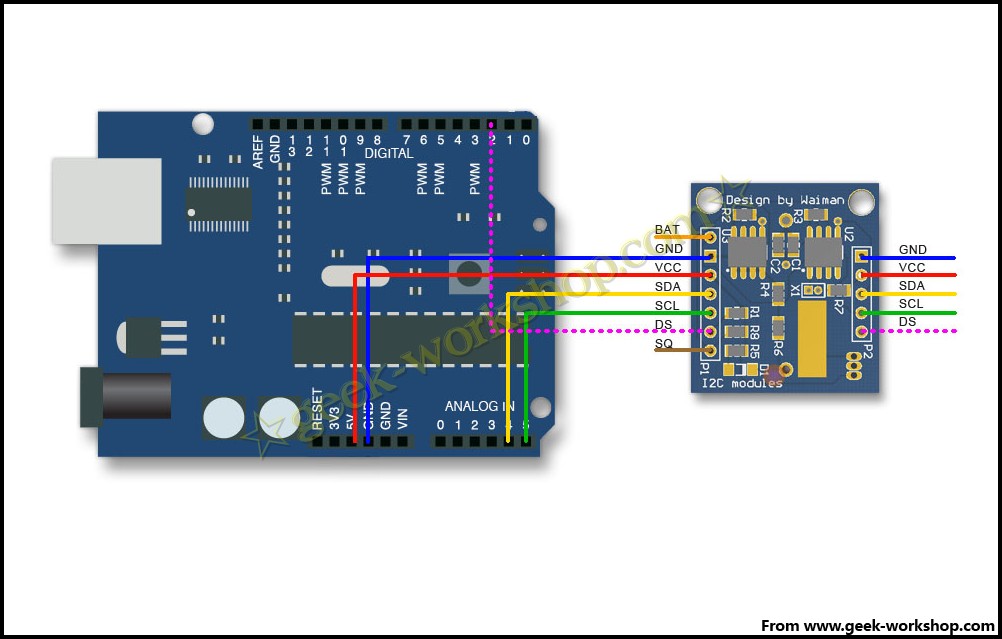
再看下硬件连接图,DS1307是I2C接口SCL接模拟5号口,SDA接模拟4号口。DS18B20是单总线模式,他的DS接口接数字2号口。
2011-11-17 22:28 上传
(104.16 KB)

2011-11-17 22:28 上传
(119.4 KB)
DS18B20:

2011-11-21 22:26 上传
(216.3 KB)
DS18x20系列数字温度传感器主要有DS18S20和DS18B20(DS18S20只有9位一种工作模式,分辨率只到0.5摄氏度,DS18B20有9、10、11、12位四种工作可编程控制的模式,分辨率最高为0.0625摄氏度。),都是由美国Dallas半导体公司(现在改名叫Maxim)生产的。这个系列最大的特点就是采用了Maxim的专利技术1-Wire。顾名思义,1-Wire就是采用单一信号线,但可像I2C,SPI一样,同时传输时钟(clock)又传输数据(data),而且数据传输是双向的。1-Wire 使用较低的数据传输速率,通常是用来沟通小型device,如数位温度计。通过1-Wire技术可以在单一信号线的基础上构成传感器网络,Maxim起名”MicroLan”。
DS18x20的供电主要有两种模式:
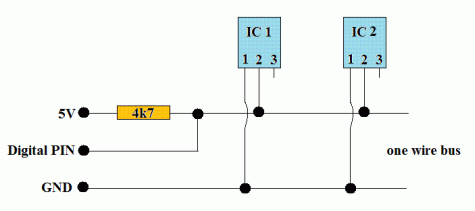
Parasite power mode/寄生供电
2011-11-18 11:13 上传
(8.09 KB)
所谓的寄生供电是指DS18x20只需要两根接线,一根数据线,一根接地线,数据线上还要接一个4.7k上拉电阻连电源,数据线同时也提供了电能。DS18x20内置了电容,高电平期时把电能储存在内部电容里,低电平期内消耗内部电容里的能量工作,直到下次高电平期内再次电容充电。虽然这样的模式简化了线路同时也带来了一些缺陷:
- 电路的电流一般很小,只有当DS18x20进行温度转化或者写EEPROM时会高达1.5mA,当DS18x20进行上述操作时,数据线必须保持电平拉高状态直到操作结束,期间master端的Arduino不能做任何操作,DS18x20温度转化时这个时间间隔大概是750ms。
2.如果要求DS18x20有精确的转化,数据线在温度转化期间必须保证足够的能量,但当你使用多个DS18x20构成MicroLan进行多点测温时,单靠4.7k的上拉电阻无法提供足够的能量,会导致较大的测温误差。
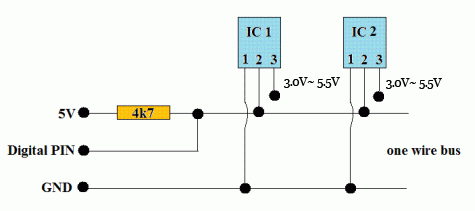
Normal (external supply) mode/标准(外部供电)
2011-11-18 11:13 上传
(17.59 KB)
标准外部供电模式,相比寄生供电模式,每个DS18x20需要多一条独立的电源线接独立电源。虽然多用些线,但由于外部供电,保证了每个设备的进精确度和稳定性。而且没有了上述温度转换期间Arduino不能做任何事的问题。
DS18B20的详细介绍就不多讲了,具体可以查看论坛的另一篇帖子
http://www.geek-workshop.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=198&extra=page%3D1
直接进入实战,调用DS18B20,需要使用OneWire库。
把下面代码下载进入arduino控制板。ARDUINO 代码复制打印
#include <OneWire.h>
// DS18S20 Temperature chip i/o
OneWire ds(2); // on pin 2
void setup(void) {
// initialize inputs/outputs
// start serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
}
void loop(void) {
byte i;
byte present = 0;
byte data[12];
byte addr[8];
if ( !ds.search(addr)) {
Serial.print("No more addresses.\n");
ds.reset_search();
return;
}
Serial.print("R=");
for( i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
Serial.print(addr[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
if ( OneWire::crc8( addr, 7) != addr[7]) {
Serial.print("CRC is not valid!\n");
return;
}
if ( addr[0] == 0x10) {
Serial.print("Device is a DS18S20 family device.\n");
}
else if ( addr[0] == 0x28) {
Serial.print("Device is a DS18B20 family device.\n");
}
else {
Serial.print("Device family is not recognized: 0x");
Serial.println(addr[0],HEX);
return;
}
ds.reset();
ds.select(addr);
ds.write(0x44,1); // start conversion, with parasite power on at the end
delay(1000); // maybe 750ms is enough, maybe not
// we might do a ds.depower() here, but the reset will take care of it.
present = ds.reset();
ds.select(addr);
ds.write(0xBE); // Read Scratchpad
Serial.print("P=");
Serial.print(present,HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // we need 9 bytes
data[i] = ds.read();
Serial.print(data[i], HEX);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.print(" CRC=");
Serial.print( OneWire::crc8( data, 8), HEX);
Serial.println();
}
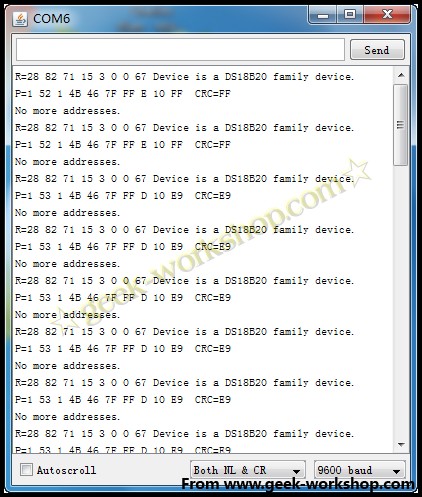
代码下载好以后打开串口编辑器,然后就会出现下面这样子的画面。
2011-11-18 23:46 上传
(79.63 KB)
虽然我们读到了Scratchpad的数据,但是显示的是HEX16进制代码,我们还需要转化成我们能读的温度格式。这里推荐一个叫Dallas Temperature Control的Library,大大简化了这个过程。官方地址:
http://www.milesburton.com/?title=Dallas_Temperature_Control_Library
ARDUINO 代码复制打印
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
// Data wire is plugged into port 2 on the Arduino
#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 2
// Setup a oneWire instance to communicate with any OneWire devices (not just Maxim/Dallas temperature ICs)
OneWire oneWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);
// Pass our oneWire reference to Dallas Temperature.
DallasTemperature sensors(&oneWire);
void setup(void)
{
// start serial port
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("Dallas Temperature IC Control Library Demo");
// Start up the library
sensors.begin();
}
void loop(void)
{
// call sensors.requestTemperatures() to issue a global temperature
// request to all devices on the bus
Serial.print("Requesting temperatures...");
sensors.requestTemperatures(); // Send the command to get temperatures
Serial.println("DONE");
Serial.print("Temperature for the device 1 (index 0) is: ");
Serial.println(sensors.getTempCByIndex(0));
}
代码下载好以后,打开串口监视器,就可以看到当前室温了。
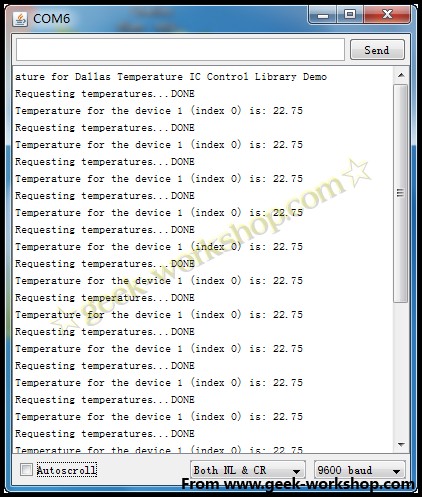
2011-11-18 23:46 上传
(81.57 KB)
下面我们试用一下DS1307时钟芯片功能。
先把下面库自带测试代码下载进入arduino控制板ARDUINO 代码复制打印
#include <WProgram.h>
#include <Wire.h>
#include <DS1307.h>
int rtc[7];
int ledPin = 13;
void setup()
{
DDRC|=_BV(2) |_BV(3); // POWER:Vcc Gnd
PORTC |=_BV(3); // VCC PINC3
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.begin(9600);
RTC.stop();
RTC.set(DS1307_SEC,1);
RTC.set(DS1307_MIN,57);
RTC.set(DS1307_HR,17);
RTC.set(DS1307_DOW,2);
RTC.set(DS1307_DATE,18);
RTC.set(DS1307_MTH,1);
RTC.set(DS1307_YR,10);
RTC.start();
}
void loop()
{
RTC.get(rtc,true);
for(int i=0; i<7; i++)
{
Serial.print(rtc[i]);
Serial.print(" ");
}
Serial.println();
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(500);
}
然后打开串口监视器,就能看到类似下图的样子。
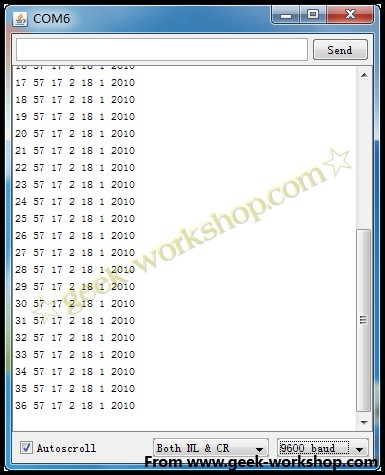
2011-11-20 20:45 上传
(51.22 KB)
这个模块上还有一个T24C32A EEPROM存储器。。。下面上一个全面一点的代码,对各个期间进行测试。其中刚开始会对I2C器件进行扫描。。。代码不错,大家可以参考下。ARDUINO 代码复制打印
/**
* I2CScanner.pde -- I2C bus scanner for Arduino
*
* 2009, Tod E. Kurt, [url]http://todbot.com/blog/[/url]
*
*/
#include <OneWire.h>
#include "Wire.h"
#include <WProgram.h>
#include <DS1307.h>
#include <avr/io.h>
extern "C" {
#include "utility/twi.h" // from Wire library, so we can do bus scanning
}
byte start_address = 1;
byte end_address = 127;
OneWire ds(2); // on pin 2
byte Tdata[12];
int sensorValue = 0; // value read from the pot
int rtc[7];
float TT=0.0;
// Scan the I2C bus between addresses from_addr and to_addr.
// On each address, call the callback function with the address and result.
// If result==0, address was found, otherwise, address wasn't found
// (can use result to potentially get other status on the I2C bus, see twi.c)
// Assumes Wire.begin() has already been called
void scanI2CBus(byte from_addr, byte to_addr,
void(*callback)(byte address, byte result) )
{
byte rc;
byte data = 0; // not used, just an address to feed to twi_writeTo()
for( byte addr = from_addr; addr <= to_addr; addr++ ) {
rc = twi_writeTo(addr, &data, 0, 1);
if(rc==0) callback( addr, rc );
}
}
// Called when address is found in scanI2CBus()
// Feel free to change this as needed
// (like adding I2C comm code to figure out what kind of I2C device is there)
void scanFunc( byte addr, byte result ) {
Serial.print("addr: ");
Serial.print(addr,DEC);
addr = addr<<1;
Serial.print("\t HEX: 0x");
Serial.print(addr,HEX);
Serial.println( (result==0) ? "\t found!":" ");
// Serial.print( (addr%4) ? "\t":"\n");
}
void i2c_eeprom_write_byte( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress, byte data ) {
int rdata = data;
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.send((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // MSB
Wire.send((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // LSB
Wire.send(rdata);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
// WARNING: address is a page address, 6-bit end will wrap around
// also, data can be maximum of about 30 bytes, because the Wire library has a buffer of 32 bytes
void i2c_eeprom_write_page( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddresspage, byte* data, byte length ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.send((int)(eeaddresspage >> 8)); // MSB
Wire.send((int)(eeaddresspage & 0xFF)); // LSB
byte c;
for ( c = 0; c < length; c++)
Wire.send(data[c]);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
byte i2c_eeprom_read_byte( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress ) {
byte rdata = 0xFF;
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.send((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // MSB
Wire.send((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // LSB
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(deviceaddress,1);
if (Wire.available()) rdata = Wire.receive();
return rdata;
}
// maybe let's not read more than 30 or 32 bytes at a time!
void i2c_eeprom_read_buffer( int deviceaddress, unsigned int eeaddress, byte *buffer, int length ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(deviceaddress);
Wire.send((int)(eeaddress >> 8)); // MSB
Wire.send((int)(eeaddress & 0xFF)); // LSB
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(deviceaddress,length);
int c = 0;
for ( c = 0; c < length; c++ )
if (Wire.available()) buffer[c] = Wire.receive();
}
void DS1302_SetOut(byte data ) {
Wire.beginTransmission(B1101000);
Wire.send(7); // LSB
Wire.send(data);
Wire.endTransmission();
}
byte DS1302_GetOut(void) {
byte rdata = 0xFF;
Wire.beginTransmission(B1101000);
Wire.send(7); // LSB
Wire.endTransmission();
Wire.requestFrom(B1101000,1);
if (Wire.available()) {
rdata = Wire.receive();
Serial.println(rdata,HEX);
}
return rdata;
}
void showtime(void){
byte i;
Serial.print("Time=");
DS1302_SetOut(0x00);
RTC.get(rtc,true);
for(int i=0; i<7; i++) {
Serial.print(rtc[i]);
Serial.print(" ");
}
}
void readBatVcc(void){
sensorValue = analogRead(A1);
TT = sensorValue*0.0047;
Serial.print("Battery: ");
Serial.print(TT);
Serial.print("V");
}
// standard Arduino setup()
void setup()
{
DDRC|=_BV(2) |_BV(3);
PORTC |=_BV(3);
Wire.begin();
Serial.begin(19200);
Serial.println("--- I2C Bus Scanner Test---");
Serial.print("starting scanning of I2C bus from ");
Serial.print(start_address,DEC);
Serial.print(" to ");
Serial.print(end_address,DEC);
Serial.println("...");
// start the scan, will call "scanFunc()" on result from each address
scanI2CBus( start_address, end_address, scanFunc );
Serial.println("\n");
Serial.println("--- EEPROM Test---");
char somedata[] = "this is data from the eeprom"; // data to write
i2c_eeprom_write_page(0x50, 0, (byte *)somedata, sizeof(somedata)); // write to EEPROM
delay(100); //add a small delay
Serial.println("Written Done");
delay(10);
Serial.print("Read EERPOM:");
byte b = i2c_eeprom_read_byte(0x50, 0); // access the first address from the memory
int addr=0; //first address
while (b!=0)
{
Serial.print((char)b); //print content to serial port
addr++; //increase address
b = i2c_eeprom_read_byte(0x50, addr); //access an address from the memory
}
Serial.println("\n");
Serial.println("");
Serial.println("--- DS11307 RTC Test---");
showtime();
if(rtc[6]<2011){
RTC.stop();
RTC.set(DS1307_SEC,1);
RTC.set(DS1307_MIN,52);
RTC.set(DS1307_HR,16);
RTC.set(DS1307_DOW,2);
RTC.set(DS1307_DATE,25);
RTC.set(DS1307_MTH,1);
RTC.set(DS1307_YR,11);
RTC.start();
Serial.println("SetTime:");
showtime();
}
Serial.println("\n\n");
Serial.println("--- Reserve Power Test---");
Serial.println(" Close POWER!:");
PORTC &=~_BV(3);
byte time;
for(time=0;time<5;time++){
digitalWrite(13,HIGH);
delay(500);
digitalWrite(13,LOW);
delay(500);
readBatVcc();
Serial.println("");
}
PORTC |=_BV(3);
Serial.println("\n POWER On!");
delay(500);
showtime();
Serial.println("\n");
Serial.println("=== Done ===");
Serial.println("\n");
}
// standard Arduino loop()
void loop()
{
byte i;
byte present = 0;
unsigned int Temper=0;
readBatVcc();
ds.reset();
ds.write(0xCC,1);
ds.write(0x44,1); // start conversion, with parasite power on at the end
digitalWrite(13,HIGH);
delay(450);
digitalWrite(13,LOW);
delay(450);
present = ds.reset();
ds.write(0xCC,1);
ds.write(0xBE); // Read Scratchpad
for ( i = 0; i < 9; i++) { // we need 9 bytes
Tdata[i] = ds.read();
}
Temper = (Tdata[1]<<8 | Tdata[0]);
TT =Temper*0.0625;
if(TT>200){
Serial.println("\t DS18B20 Not installed!");
}else{
Serial.print("\t Temperature=");
Serial.println(TT);
}
Serial.println("");
}
然后打开串口监视器,波特率要调节为19200.
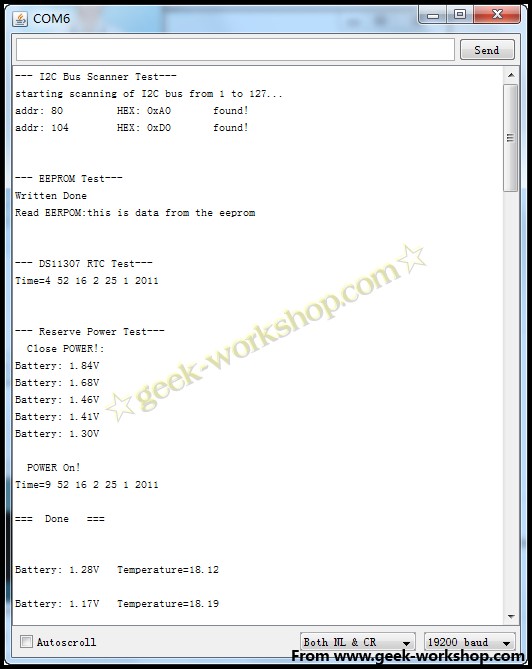
2011-11-20 20:45 上传
(60.68 KB)
附件是这次需要用到的库(适用于0022与0023 IDE):
网盘下载附件http://pan.baidu.com/s/1dExdYV3
OneWire.rar (8.59 KB)
DS1307.rar (2.59 KB)
DallasTemperature_371Beta.zip (22.44 KB)
补充1.0.1下可用的DS180B20库
OneWire_1.0.1.zip (14.38 KB)
DallasTemperature_372Beta_1.0.1.zip (22.87 KB)
via - 极客工坊